What is ITR?
The Income Tax Return or ITR is a form in which the taxpayers submit information about their income and tax payments to the income tax department.
The ITR form applicable to a taxpayer depends on the type of taxpayer, whether individuals, HUF, company, etc., and you choose the ITR based on the nature and type of income and total income.
Due date for filing ITR
A taxpayer should file an ITR on or before the due date specified. The following table lists due dates for filing ITR to different types of assesses.
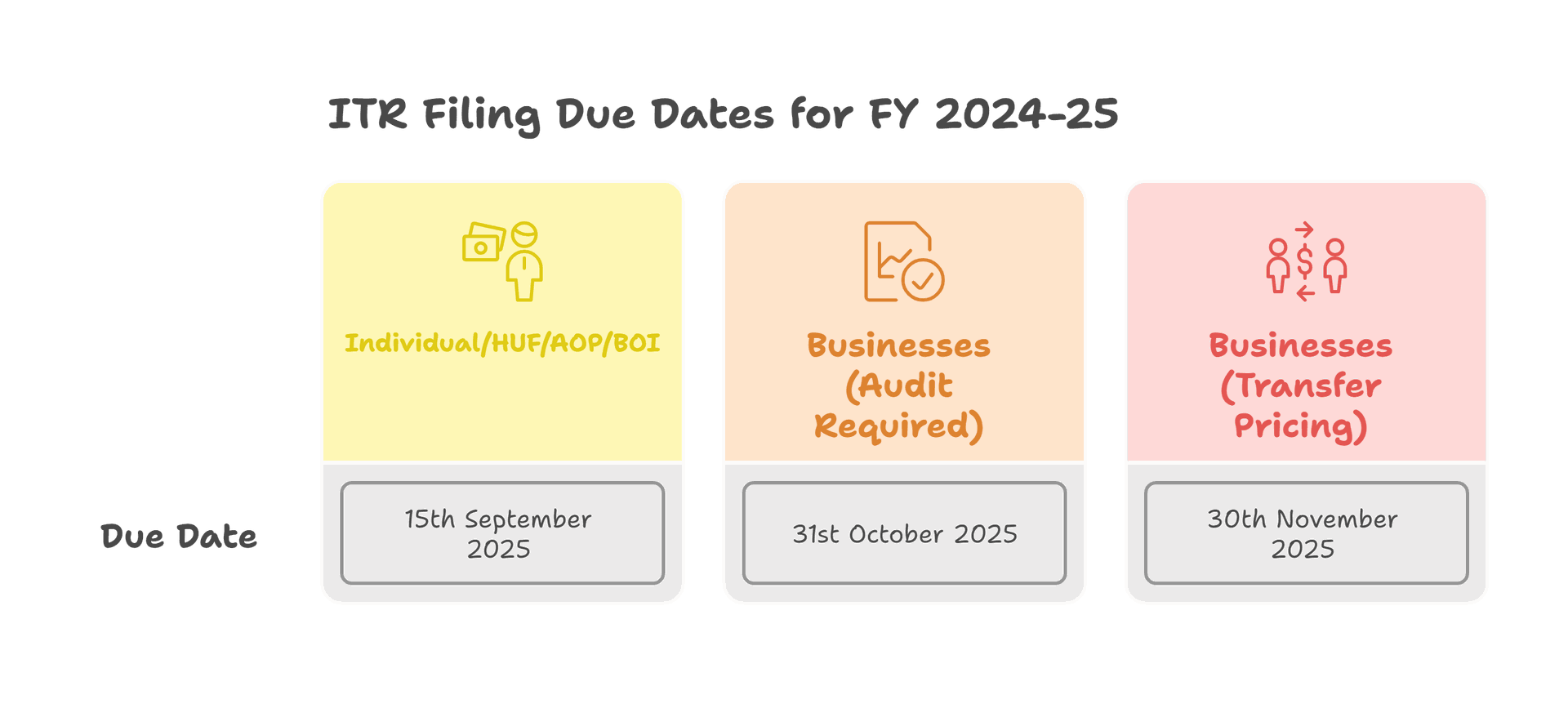
| Category of Taxpayer | Due Date for Tax Filing - FY 2024-25 *(unless extended) |
| Individual / HUF/ AOP/ BOI (books of accounts not required to be audited) | 15th September 2025 |
| Businesses (Requiring Audit) | 31st October 2025 |
| Businesses requiring transfer pricing reports (in case of international/specified domestic transactions) | 30th November 2025 |
While filing your ITR, you should check the form 26AS for details of TDS and other income such as FD interest. You should also have your form 16 to enable filling the details of salary and tax saving deduction claims.
Documents Required to File ITR
Depending on the tax bracket the individual falls under, the list of documents that are needed will differ. Some of the common list of documents that are needed to file ITR are mentioned below:
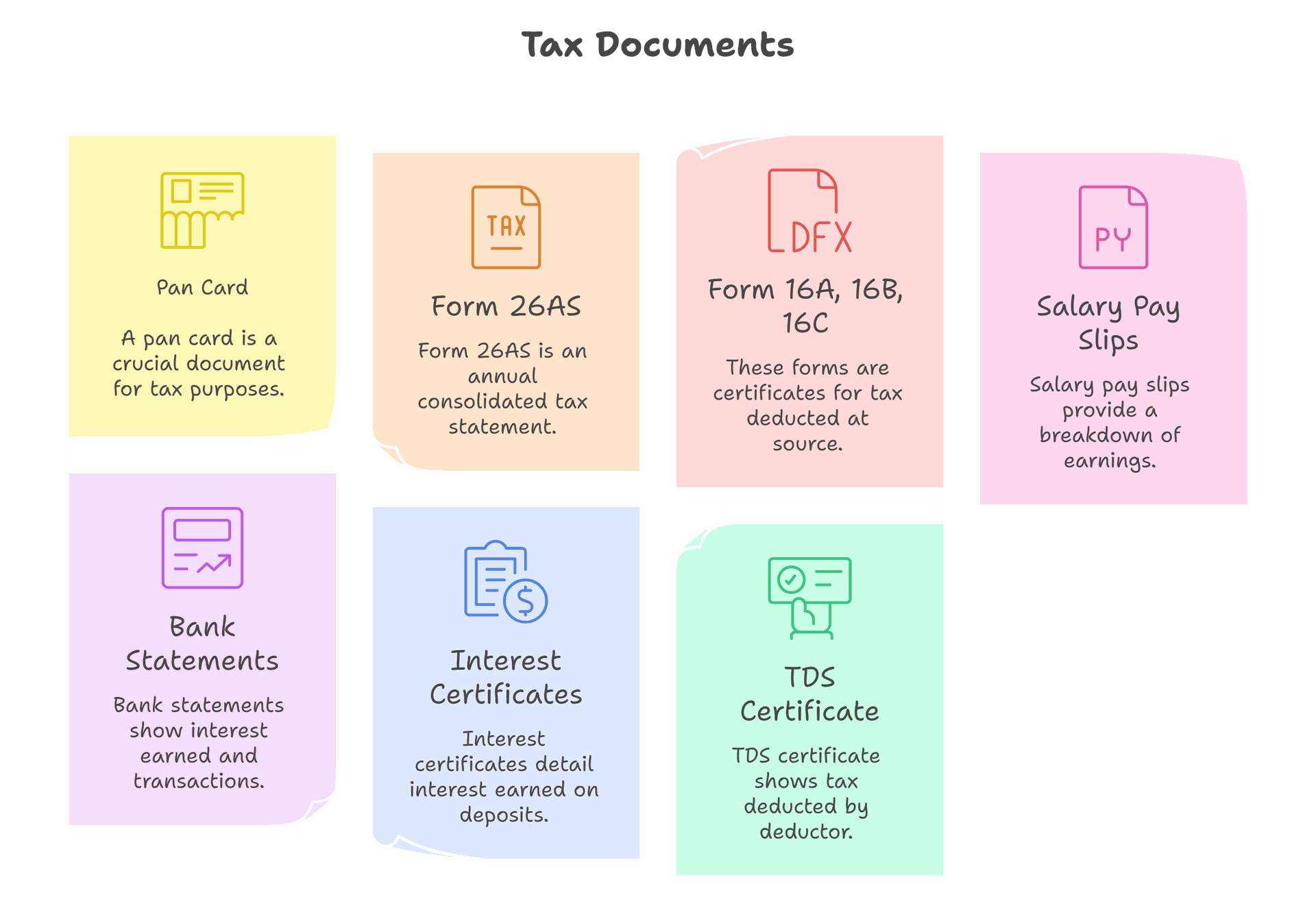
- Pan card
- Form 26AS
- Form 16A, 16B, 16C
- Salary Pay slips
- Bank statements
- Interest certificates
- TDS certificate
- Proof of Tax Saving Investments
Types of ITR
A taxpayer should file an ITR on or before the due date specified. The following table lists due dates for filing ITR to different types of assesses.
| ITR Form | Persons required to file |
| ITR-1 (Sahaj) | For resident individuals with income within Rs. 50 lakh from salary, one house property, section 112A capital gains up to Rs. 1.25 lakhs and other sources (excluding business/profession). |
| ITR-2 | For individuals and HUFs not having income from business or profession, but having capital gains, foreign income/assets, or income above Rs. 50 lakh, owning unlisted shares and being director of any company. |
| ITR-3 | For individuals and HUFs with income from business or profession, including those opting out of presumptive taxation. |
| ITR-4 (Sugam) | For individuals, HUFs, and firms (other than LLPs) opting for presumptive taxation. |
| ITR-5 | Exclusively for Firms, Local authorities, Co-operative societies, Artificial Judicial persons, Body of individuals. |
| ITR-6 | For Organizations or Companies other than those claiming exemption under Section 11 (Income from property held for charitable or religious purposes), ITR-6 has to be filed electronically only. |
| ITR-7 | For entities claiming exemption, such as colleges, universities, scientific research institutions, charitable or religious trusts, political parties, and similar organizations and filing under Section 139(4A), 139(4B), 139(4C), 139(4D) |
Who to File ITR?
You can e-file your ITR for the FY 2024-25 corresponding to the AY 2025-26. The filing is mandatory for all types of taxpayers except in the following cases.
- Taxpayers aged 75 or above and satisfying the following conditions
- Pension and interest income are the only sources of total income. Interest income can be from any account maintained with the same bank in which they receive pension.
- They have submitted a declaration to the bank.
- Such bank deducts TDS under Section 194P.
- Taxpayers with an income less than the applicable basic exemption limit.
Types of Forms for ITR E-filing
Form 16: Form 16 is a salary TDS certificate an employee receives from the employer. Form 16 provides the details of gross salary and exemptions such as HRA and LTA. The form also contains the details of the net taxable salary, any other income/loss reported by the employee, tax saving deductions and salary TDS.
Form 26AS: Form 26AS contains details of tax deducted at source or TDS on various incomes such as salary, interest, and the sale of immovable property. The form also contains details of self-assessment tax, advance tax paid by a taxpayer, and specified financial transactions.
Form 15G and Form 15H: Form 15G and Form 15H enable you to receive income without TDS. You can submit Form 15G in case you are below 60 years of age and where your annual taxable income is below the basic exemption limit. You can submit Form 15H in the case where you are a senior citizen and the tax due on your total income is nil. You need to submit form 15G or form 15H to the person paying you income.
Why Should You File ITR?
It is mandatory for one to file income tax returns in India if he comes under any of the following conditions:
- Individuals who fall within the respective tax slabs.
- If it's a Company or Firm, irrespective of the profit or loss made in a financial year.
- If a tax refund needs to be claimed.
- If a loss under a head of income needs to be carried forward.
- If one is applying for a loan or a visa.
- If being a resident of India, one has an asset or financial interest in any entity located outside India & one is a signing authority in a foreign account.
- If an NRI derives any or all of his/her income through sources in India, that income is liable to be taxable in India.
- If one receives income derived from property held under a trust for charitable or religious purposes or a political party or a research association, news agency, educational or medical institution, trade union, a not-for-profit university or educational institution, a hospital, infrastructure debt fund, any authority, body or trust.
How to file ITR?
ITR can be filed in the income tax portal by logging into the taxpayers account. The following steps are recommended to be followed while filing ITR
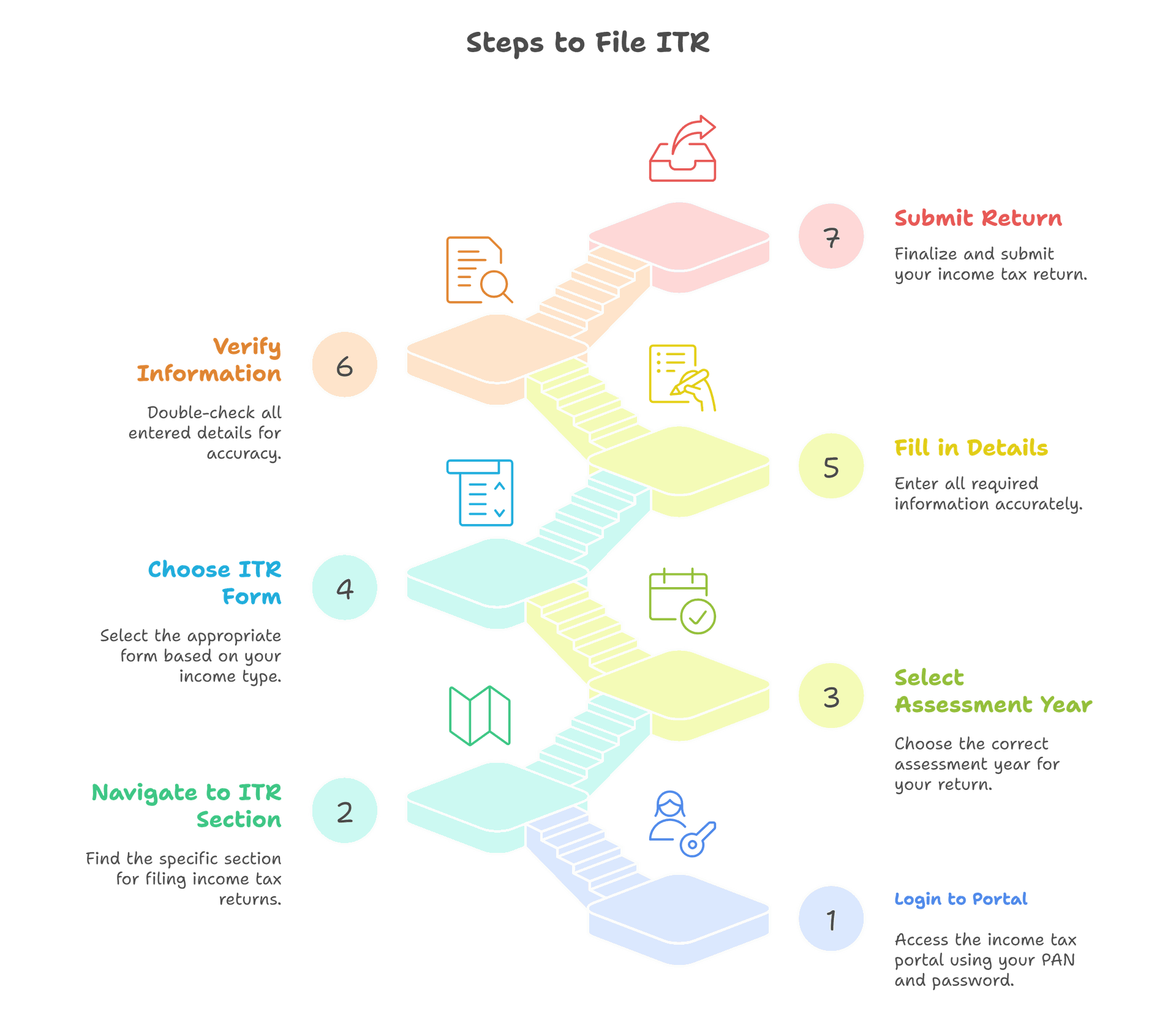
Step 1: Login to the Income Tax portal using your PAN as the login ID and password as encrypted.
Step 2: On the home page, go to 'e-File' tab > 'Income Tax Returns' > ‘File Income Tax Return’.
Step 3: Select the correct Assessment Year. The assessment year for FY 2024-25 is 2025-26.
Step 4: Select Filing Status - whether you are individual, HUF, or any other kind of assesses. Mostly for salaried and freelancing taxpayers, 'Individuals may be chosen.
Step 5: Select ITR Type, depending on your income level
Step 6: Select Reason for filing ITR. You may file because of the taxable income has crossed the exemption limit or on satisfaction of specified conditions.
Step 7: Enter your personal details, bank account details, income earned, deductions claimed and taxes paid. Cross verify the summary for accuracy and proceed filing the return.
Step 8: On successful completion of e-filing, the last step is e-verification.
Conclusion
Filing your Income Tax Return (ITR) is not just a legal obligation but also offers several financial benefits. Ensure you file your ITR on time, choose the correct form, and keep all necessary documents handy for a hassle-free experience. For more information and to file your ITR online, visit the official Income Tax e-Filing Portal.